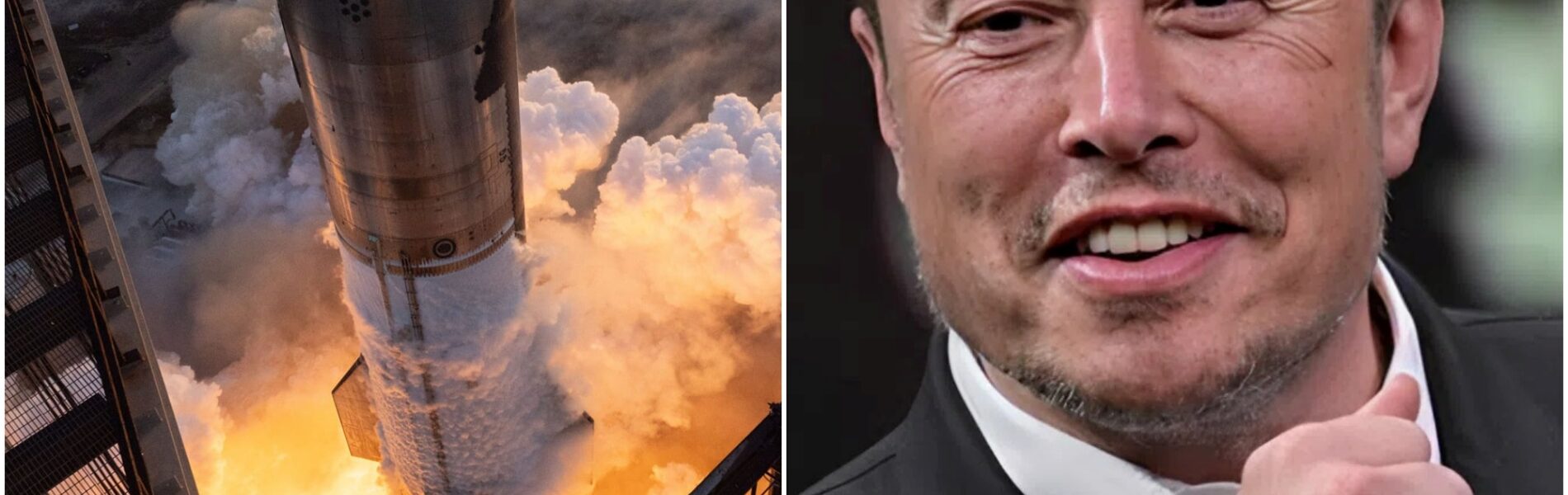
After Months of Explosive Failures, SpaceX Celebrates Starship’s First True Success
Cape Canaveral, FL – For months, SpaceX’s most ambitious project, the Starship launch vehicle, was synonymous with fiery explosions, mid-air disintegrations, and shattered hopes. But on its most recent mission, the company achieved what once seemed elusive: Starship soared into space, successfully deployed a set of satellites, and returned safely to Earth. The breakthrough marks a turning point not only for SpaceX but for the future of human space exploration.

A Long Road Paved With Failures
SpaceX’s Starship program has always been billed as the crown jewel of Elon Musk’s space ambitions—a fully reusable spacecraft capable of carrying 100 tons of cargo, ferrying astronauts to the Moon and Mars, and revolutionizing commercial launches. But for years, the dream appeared out of reach.
From the outside, the failures looked catastrophic. Test flights ended in spectacular explosions on live streams. Prototypes either failed to reach orbit, lost control during descent, or collapsed in fireballs upon landing. Critics questioned whether the company’s bold vision was technically achievable—or merely hubris wrapped in stainless steel.
The early prototypes—SN8 through SN15—provided valuable data but rarely produced clean results. Each explosion became viral fodder, spawning memes and fueling skepticism. Yet engineers inside SpaceX insisted that failure was part of the design philosophy. “We build, we test, we break things, and then we learn,” one engineer remarked at the time.
The Anatomy of Past Failures
1. Propellant Instabilities
One recurring issue was the instability of liquid methane and oxygen propellants under extreme conditions. During early test flights, unexpected pressure fluctuations caused engines to lose thrust. At times, engines shut down prematurely, dooming missions before reaching target altitudes.
2. Heat Shield Vulnerabilities
On re-entry, prototypes faced extreme aerodynamic heating. Tiles designed to shield the spacecraft either detached or cracked, allowing heat to compromise internal structures. Several vehicles lost stability and disintegrated before reaching landing zones.
3. Landing System Failures
Even when ascent and descent seemed successful, Starship prototypes faltered at the last moment. Landing legs failed to deploy, or thrust controls misfired, resulting in the spacecraft tipping over and exploding on contact. These “near misses” frustrated engineers but highlighted flaws in the vehicle’s last stage design.
4. Integration and Deployment Issues
In attempts to simulate payload deployment, previous tests encountered separation malfunctions. Some satellites failed to eject, while others were released incorrectly, undermining confidence in Starship’s utility for commercial missions.
What Changed This Time?
SpaceX’s latest mission was different because of a series of key engineering overhauls and lessons absorbed from those painful failures.
1. Refined Raptor Engines
At the heart of Starship are its Raptor engines. Early versions were prone to combustion instabilities. The latest iteration, Raptor 3, boasts more efficient fuel pumps, sturdier turbomachinery, and real-time adaptive controls. These changes provided steadier thrust, eliminating the shutdown issues that plagued earlier flights.
2. Next-Generation Heat Shield Tiles
Engineers redesigned heat-resistant tiles using a new ceramic composite material. Lighter and more durable, these tiles were mounted with flexible fasteners that allowed micro-movements during re-entry, preventing cracks or detachments. For the first time, the shield endured the full intensity of re-entry without catastrophic loss.
3. Automated Landing Algorithms
The landing process was overhauled with upgraded flight software capable of micro-second adjustments. The new system factored in wind shear, propellant sloshing, and engine response delay. The result: Starship touched down smoothly, supported by redesigned landing legs with wider bases for stability.

4. Payload Deployment Mechanisms
Perhaps the most critical improvement was the re-engineered payload bay. A modular deployment system, tested extensively in vacuum chambers, allowed satellites to eject with precision. In the successful mission, every payload deployed into its intended orbit—an achievement that confirmed Starship’s commercial viability.
The Mission: A Milestone for SpaceX
On launch day, the mood was cautious optimism. Spectators who had grown used to seeing fiery ends held their breath as the rocket ignited. Starship roared into the sky, its Raptor engines blazing bright but controlled. Minutes later, cheers erupted at mission control: the vehicle had passed Max Q, the point of maximum aerodynamic stress—a point where many previous prototypes failed.
As the vehicle separated and continued toward orbit, engineers watched telemetry anxiously. Hours later, satellites were deployed in perfect sequence. Finally, the ultimate test: re-entry and landing. The heat shield glowed but held firm, the ship slowed, and in a plume of dust and fire, Starship landed upright. No explosion. No collapse. Just triumph.
Reactions From Musk and Beyond
Elon Musk, who had faced relentless criticism during the program’s turbulent years, was visibly emotional. “This is the beginning of a new era,” he tweeted moments after touchdown. “Starship will take humanity to Mars—and it starts today.”
NASA officials, who have invested billions in Starship for future Artemis missions to the Moon, welcomed the news. “This successful test is a huge confidence boost,” said NASA Administrator Bill Nelson. “Starship is a cornerstone of our lunar ambitions.”
Space industry analysts agreed. “If Starship can reliably repeat this performance, it will reset the economics of spaceflight,” said Dr. Laura Cheng, aerospace engineer at MIT. “The ability to launch massive payloads cheaply and reuse the vehicle changes everything.”
The Road Ahead
SpaceX is not celebrating for long. The company plans multiple follow-up flights in the next year, with progressively more complex objectives: carrying larger payloads, performing in-space refueling, and eventually transporting astronauts.
Challenges remain. Regulatory approval from the FAA is contingent on ongoing safety evaluations. Communities near launch sites continue to express concerns about noise, environmental impact, and safety risks. And skeptics caution that one successful mission does not erase years of setbacks.
Still, momentum has shifted. Investors, previously nervous, are showing renewed interest. Satellite companies are lining up for launch slots. And among the public, enthusiasm has surged—millions tuned in to the livestream, celebrating SpaceX’s long-awaited breakthrough.
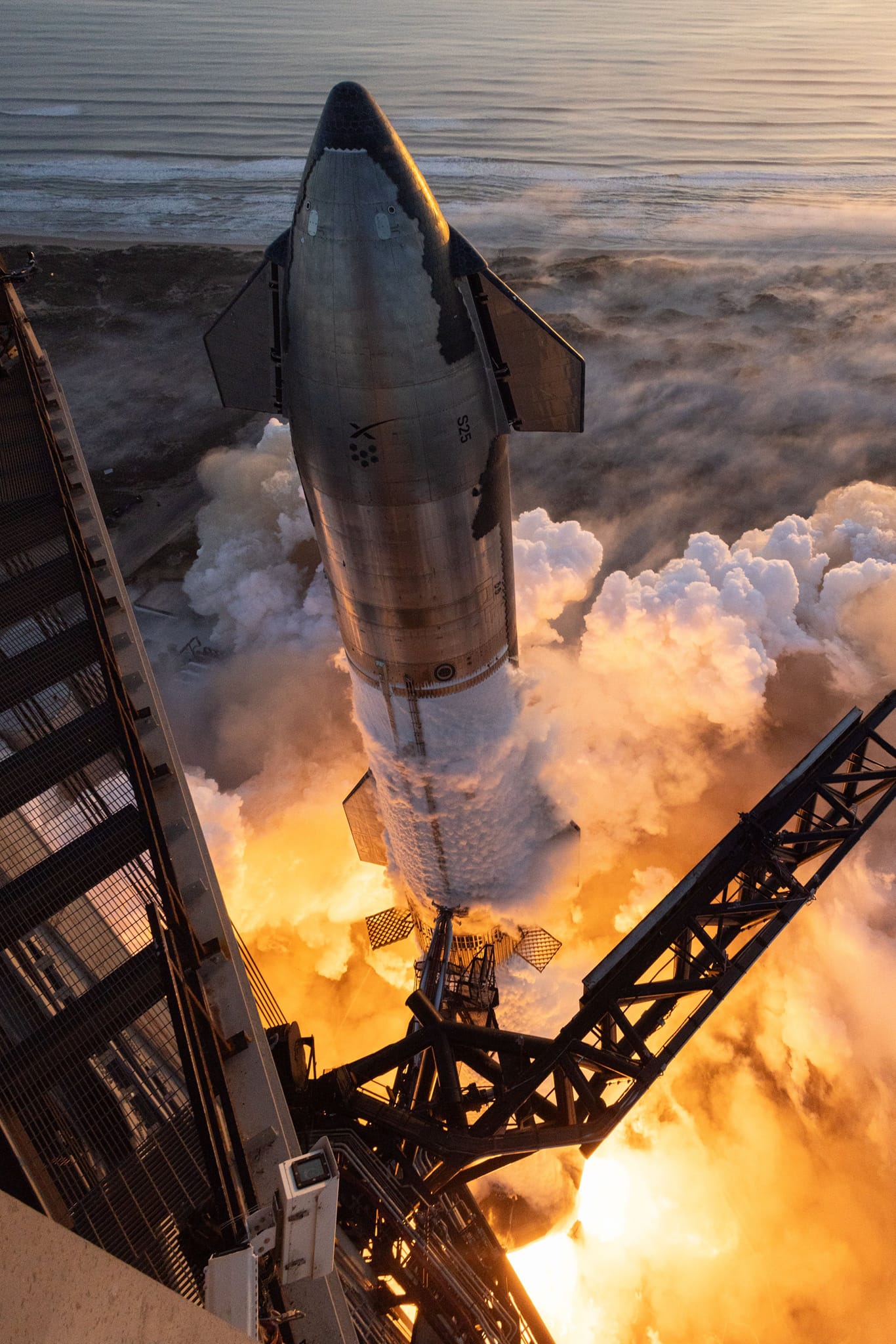

Why This Success Matters
Starship’s success is not just about one company’s reputation. It is about the next frontier of space exploration. NASA’s Artemis program aims to land astronauts on the Moon within the decade. Mars remains Elon Musk’s personal obsession, but scientists see genuine potential in a vehicle capable of carrying large crews and habitats.
Beyond exploration, Starship promises practical applications: launching massive constellations of satellites, building space stations, enabling intercontinental “point-to-point” travel on Earth, and transporting humanitarian supplies across the globe.
“SpaceX has given us a glimpse of what a truly reusable, super-heavy vehicle can do,” said Dr. Cheng. “It’s the difference between occasional voyages and a regular space economy.”

Conclusion
After years of fiery wrecks and failed attempts, SpaceX’s Starship has finally delivered. The latest mission not only reached orbit and deployed satellites but returned intact—a feat many thought impossible.
By learning from its failures—improving engines, heat shields, software, and payload systems—SpaceX has turned embarrassment into triumph. For Elon Musk, it is vindication. For NASA and the global space community, it is a game-changer.
Starship’s journey is far from over, but for now, one thing is certain: history will remember this mission as the day SpaceX’s dream of building a pathway to the stars stopped exploding on the launchpad and finally took flight.